In the realm of modern medicine, few substances prompt as much intrigue and controversy as Nembutal. Known primarily for its key role in anesthesia and its historical associations with euthanasia, this powerful barbiturate has a complex legacy that warrants a closer look. What exactly is Nembutal, and how has it evolved in its applications within contemporary healthcare? As we delve into its pharmacological properties and explore its various uses—from pain management to its implications in end-of-life care—this article aims to unravel the enigma surrounding Nembutal. Join us on a journey to understand not just a drug, but a pivotal element in ongoing debates about ethics and medicine. Whether you’re a medical professional or simply curious about its implications, unpacking the layers of Nembutal’s role in today’s healthcare landscape may reveal insights that are both enlightening and essential.
The Historical Context of Nembutal
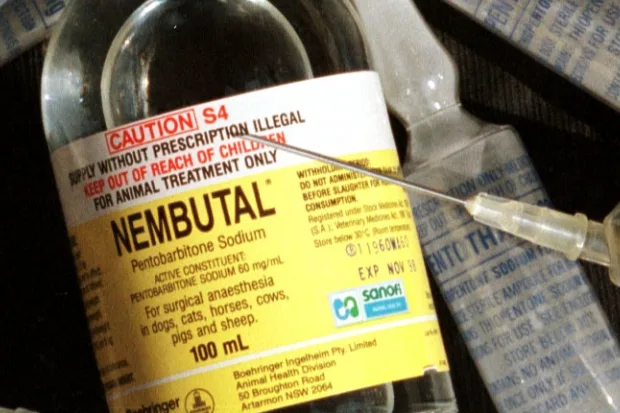
Nembutal, chemically known as pentobarbital, was first synthesized in the early 20th century by Ernst Preiswerk and Hans Joachim von Braun. This barbiturate quickly gained recognition for its potent sedative and hypnotic properties. Initially, it was hailed as a breakthrough in anesthesia and sleep medicine, marking a significant advancement in the ability to induce sleep and manage pain effectively. During the 1930s and 1940s, Nembutal became widely used in clinical settings, providing a reliable means of sedation for surgeries and other medical procedures.
As its popularity grew, Nembutal found additional applications in the treatment of insomnia and anxiety. The drug’s ability to depress the central nervous system made it an effective tool for calming patients and inducing a restful state. However, the very qualities that made Nembutal effective also contributed to its potential for misuse. Over time, the medical community began to recognize the risks associated with Nembutal, particularly its high potential for dependence and overdose.
Despite these concerns, Nembutal’s role in medicine continued to evolve. By the mid-20th century, it had become a common fixture in both human and veterinary medicine. Its use extended beyond anesthesia to include the treatment of severe epilepsy and the management of acute trauma. The historical context of Nembutal is thus a tale of both innovation and caution, reflecting the dual nature of many powerful pharmaceuticals.
Nembutal Composition and Mechanism of Action
Nembutal belongs to the barbiturate class of drugs, characterized by their ability to depress the central nervous system. Chemically, Nembutal is a derivative of barbituric acid, with the addition of a pentyl group enhancing its lipophilicity. This structural modification allows Nembutal to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively, leading to its potent effects on the brain and nervous system.
The mechanism of action of Nembutal involves binding to the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the brain. GABA is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, and its activation leads to increased chloride ion influx into neurons. This hyperpolarizes the neurons, making them less likely to fire and thereby exerting a calming effect on the brain. Nembutal enhances the inhibitory effects of GABA, resulting in profound sedation and hypnotic states.
The pharmacokinetics of Nembutal also play a crucial role in its clinical efficacy. After administration, Nembutal is rapidly absorbed and distributed throughout the body, with peak plasma concentrations occurring within minutes. Its relatively short half-life makes it suitable for procedures requiring brief but intense sedation. However, this same characteristic necessitates careful dosing and monitoring to avoid adverse effects.
Medical Uses of Pentobarbital in Contemporary Medicine
In modern medicine, Nembutal continues to be used primarily for its anesthetic and sedative properties. One of its most common applications is in the induction of anesthesia for surgical procedures. Due to its rapid onset and potent effects, Nembutal is often employed to quickly sedate patients before they are transitioned to longer-acting anesthetics. This initial sedation is crucial for ensuring patient comfort and facilitating the smooth progression of surgery.
Beyond its role in anesthesia, Nembutal is also utilized in the management of severe seizures, particularly in cases of refractory status epilepticus. When other antiepileptic drugs fail to control seizures, Nembutal can be administered to suppress neuronal activity and halt the seizure activity. This application highlights Nembutal’s importance in critical care settings, where rapid and effective intervention is necessary to prevent further neurological damage.
Nembutal’s use extends to veterinary medicine as well. It is commonly employed as an anesthetic and euthanasia agent for animals. Its ability to induce a quick and painless termination of life makes it a preferred choice in situations where humane euthanasia is necessary. This practice underscores the ethical dimensions of Nembutal’s use, reflecting its dual role as both a life-saving and life-ending drug.
Pentobarbital in Palliative Care and Euthanasia
Nembutal’s sedative and anesthetic properties have significant implications for palliative care, where the primary focus is on alleviating suffering and enhancing the quality of life for patients with terminal illnesses. In this context, Nembutal is sometimes used to manage severe pain and agitation, providing relief when other medications are insufficient. Its ability to induce deep sedation can be particularly beneficial for patients experiencing intractable symptoms, allowing them to remain comfortable during their final days.
The use of Nembutal in euthanasia is perhaps its most controversial application. In countries and states where physician-assisted suicide is legal, Nembutal is often the drug of choice for facilitating a peaceful and painless death. The drug’s rapid and potent effects ensure that patients can achieve a swift and dignified end, free from prolonged suffering. This practice has sparked intense ethical debates, with proponents arguing for the right to die with dignity and opponents raising concerns about the potential for abuse and the sanctity of life.
Legal and regulatory frameworks surrounding the use of Nembutal in euthanasia vary widely across different jurisdictions. In some places, stringent safeguards are in place to ensure that the decision to use Nembutal for euthanasia is made with full consent and after thorough consideration of all alternatives. In other regions, the use of Nembutal for this purpose remains strictly prohibited, reflecting deep-seated ethical and cultural values. The ongoing discussions about Nembutal’s role in end-of-life care highlight the complex interplay between medicine, ethics, and law.
Risks and Side Effects Associated with Nembutal
While Nembutal offers significant therapeutic benefits, its use is not without risks. One of the most concerning aspects of Nembutal is its high potential for addiction and dependence. Prolonged use of Nembutal can lead to tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects. This escalation can swiftly lead to physical dependence, making it difficult for patients to discontinue use without experiencing withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal from Nembutal can be severe and may include symptoms such as anxiety, tremors, seizures, and, in extreme cases, death.
Overdose is another critical risk associated with Nembutal. Due to its potent effects on the central nervous system, even small deviations from the prescribed dose can result in dangerous levels of sedation. Symptoms of Nembutal overdose include respiratory depression, hypotension, and coma. If not promptly treated, an overdose can be fatal. The narrow therapeutic window of Nembutal necessitates careful dosing and vigilant monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Side effects of Nembutal, even when used correctly, can also be significant. Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and impaired coordination. These effects can interfere with daily activities and pose additional risks, such as falls and accidents. More serious side effects, though less common, include allergic reactions, severe skin rashes, and liver damage. The potential for these adverse effects underscores the importance of using Nembutal only under strict medical supervision and for clearly defined indications.
Legal Status and Ethical Considerations
The legal status of Nembutal varies widely across different countries and states, reflecting diverse regulatory approaches and ethical considerations. In the United States, Nembutal is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act. This classification indicates that while Nembutal has recognized medical uses, it also carries a high potential for abuse and dependence. As a result, its distribution and use are tightly regulated, requiring prescriptions from licensed medical practitioners and adherence to strict record-keeping requirements.
In contrast, some European countries, such as the Netherlands and Belgium, have more permissive regulations regarding Nembutal, particularly in the context of euthanasia and assisted suicide. These countries have established legal frameworks that allow for the use of Nembutal to facilitate end-of-life decisions under specific conditions. These frameworks typically include safeguards such as mandatory psychiatric evaluations, second opinions from independent physicians, and thorough documentation to ensure that the decision is voluntary and well-considered. buy research chemicals online
Ethical considerations surrounding Nembutal are deeply complex and often polarizing. Proponents of its use in euthanasia argue that individuals have the right to autonomy and self-determination, including the right to choose a dignified and painless death. They contend that drug provides a humane option for those suffering from terminal illnesses or unbearable pain. Opponents, however, raise concerns about the potential for coercion, the sanctity of life, and the slippery slope that could lead to the normalization of euthanasia for non-terminal conditions. The ethical debates surrounding Nembutal reflect broader societal values and beliefs about life, death, and the role of medicine.
Alternatives to Nembutal in Medical Practice
Given the risks and controversies associated with Nembutal, medical professionals often seek alternative medications to achieve similar therapeutic outcomes. One common alternative is benzodiazepines, a class of drugs that also act on the GABA receptors but with a lower risk of overdose and dependence compared to barbiturates. Medications like lorazepam and midazolam are frequently used for sedation and anxiety management, providing a safer option for patients requiring these effects.
For anesthesia, modern practice often favors the use of anesthetic agents such as propofol and etomidate. These drugs offer rapid induction and recovery times, along with a more favorable safety profile compared to Nembutal. Propofol, in particular, is widely used in both minor and major surgical procedures due to its predictable effects and ease of titration. The development of these newer anesthetics has significantly reduced the reliance on barbiturates like Nembutal in contemporary anesthesia practice.
In the context of palliative care, opioid analgesics such as morphine and fentanyl are commonly used to manage severe pain. These medications provide robust pain relief with a well-established safety and efficacy profile when used appropriately. Additionally, non-pharmacological interventions, such as psychological support, physical therapy, and complementary therapies, play an essential role in comprehensive palliative care, addressing the multifaceted needs of patients beyond pharmacological treatment alone.
Patient Perspectives: Experiences with Nembutal
Patient experiences with Nembutal can vary widely, reflecting the diverse contexts in which the drug is used. For some patients, Nembutal provides critical relief from severe pain or anxiety, enabling them to undergo surgical procedures or manage acute medical conditions with greater comfort. Patients undergoing anesthesia with Nembutal often report a rapid and smooth induction, followed by a sense of calm and relaxation as they drift into unconsciousness. In these cases, Nembutal’s efficacy and reliability are highly valued.
In the realm of palliative care, patients and their families may view these drug as an essential tool for maintaining quality of life in the face of terminal illness. For individuals experiencing intractable pain or distress, Nembutal can offer a measure of peace and dignity during their final days. Testimonials from patients and caregivers often highlight the compassionate use of Nembutal, appreciating its ability to alleviate suffering and provide a sense of control over end-of-life decisions.
Conversely, some patients may have negative experiences with Nembutal, particularly if they encounter side effects or complications. The risk of dependence and withdrawal is a significant concern for those who use Nembutal over extended periods. Patients who have struggled with addiction to Nembutal often describe the challenges of managing withdrawal symptoms and the impact on their overall well-being. These experiences underscore the importance of careful monitoring and support for individuals using Nembutal, ensuring that the benefits of the drug are balanced against its potential risks.
Conclusion: The Future of Nembutal in Medicine
The future of the medicine is likely to be shaped by ongoing advancements in pharmacology, evolving ethical standards, and changing legal frameworks. As new anesthetic and sedative agents continue to be developed, the medical community may increasingly turn to alternatives that offer similar benefits with reduced risks. Innovations in drug delivery systems and personalized medicine could further enhance the safety and efficacy of sedation and anesthesia, potentially reducing the reliance on traditional barbiturates like Nembutal.
Ethical considerations will remain central to discussions about Nembutal’s use, particularly in the context of euthanasia and end-of-life care. As societal attitudes toward death and dying evolve, the legal and regulatory landscape may shift, influencing how Nembutal is utilized in these sensitive situations. Ongoing dialogue among healthcare professionals, ethicists, policymakers, and the public will be essential in navigating these complex issues and ensuring that patient rights and well-being are prioritized. kingpen
Ultimately, Nembutal represents both the promise and the perils of powerful pharmaceuticals. Its history and applications in modern medicine highlight the delicate balance between therapeutic benefit and potential harm. By continuing to explore and understand butal’s role in healthcare, the medical community can strive to maximize its positive impact while mitigating its risks, paving the way for more informed and compassionate patient care.